Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.308 - 315, 2020/10
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method for improving the realism and completeness of conventional PRA. However, enormous calculation costs are incurred by these improvements. One solution is to select an appropriate sampling method. In this paper, we applied the Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube, grid-point, and quasi-Monte Carlo sampling methods to the dynamic PRA of a simplified accident sequence and compared the results for each method. Quasi-Monte Carlo sampling was found to be the most effective method in this case.
Allelein, H.-J.*; Auvinen, A.*; Ball, J.*; G ntay, S.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Hidaka, Akihide; Jones, A. V.*; Kissane, M.*; Powers, D.*; Weber, G.*
ntay, S.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Hidaka, Akihide; Jones, A. V.*; Kissane, M.*; Powers, D.*; Weber, G.*
NEA/CSNI/R(2009)5, 388 Pages, 2009/12
Ishikawa, Jun; Muramatsu, Ken; Sakamoto, Toru*
JAERI-Research 2005-021, 133 Pages, 2005/09
The THALES-2 code is an integrated severe accident analysis code in order to simulate the accident progression and transport of radioactive material for probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) of a nuclear power plant, a part of a level 3 PSA being performed at JAERI for a 1,100MWe BWR-5 with a Mark-II containment. Results and insights from the analyses were that (1) the calculated release fractions of CsI and CsOH to the environment were in the range of 0.01 to 0.1 for late containment overpressure failure cases, and the release fractions for the containment venting case were one order of magnitude smaller than that of over-pressure case and those for drywell spray recovery cases where no containment failure occurred were two orders of magnitude smaller than the containment venting cases, (2) the governing factors for source terms of Iodine and Cesium are different depending on whether the containment fails before core melt or not, (3) the containment venting, which is one of the accident management measures, can be expected to reduce source terms if suppression pool bypass is avoided.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Ishikawa, Jun; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(5), p.451 - 461, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.41(Nuclear Science & Technology)The radionuclide release from MOX under severe accident conditions was investigated in VEGA program to contribute to the technical bases for safety evaluation including PSA for LWR using MOX. The MOX specimens irradiated at ATR Fugen were heated up to 3123K in helium at 0.1 and 1.0MPa. The release of volatile FP was slightly enhanced below 2200K compared with that of UO . The volatile FP release at elevated pressure was decreased as in the case with UO
. The volatile FP release at elevated pressure was decreased as in the case with UO . The total fractional release of Cs reached almost 100% while almost no release of low-volatile FP even after the fuel melting. The release rate of plutonium above 2800K increased rapidly although the amount was small. Since the existing models cannot predict this increase, an empirical model was prepared based on the data. There is no large difference in FP inventories between UO
. The total fractional release of Cs reached almost 100% while almost no release of low-volatile FP even after the fuel melting. The release rate of plutonium above 2800K increased rapidly although the amount was small. Since the existing models cannot predict this increase, an empirical model was prepared based on the data. There is no large difference in FP inventories between UO and MOX, and the fractional releases from MOX can be mostly predicted by the model for UO
and MOX, and the fractional releases from MOX can be mostly predicted by the model for UO . This suggests that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO
. This suggests that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO from a view point of risks.
from a view point of risks.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Ishigami, Tsutomu; Ishikawa, Jun; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(12), p.1192 - 1203, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)An experimental program VEGA is being performed at JAERI to understand mechanisms of radionuclides release from fuel during severe accidents and to improve source term predictability. The VEGA tests showed that the Cs release rate at 1.0MPa decreased by about 30% compared with that at 0.1MPa. To explain this pressure effect, a numerical release model on 2-stage diffusion that considers the lattice diffusion in grains followed by gaseous diffusion in open pores was newly developed and a simplified model 1/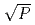 CORSOR-M was derived from the numerical model. The effect of pressure on source term was also estimated for a transient sequence at BWR with JAERI's THALES-2 code in which the simplified model was incorporated. Since the adequacy and applicability of 1/
CORSOR-M was derived from the numerical model. The effect of pressure on source term was also estimated for a transient sequence at BWR with JAERI's THALES-2 code in which the simplified model was incorporated. Since the adequacy and applicability of 1/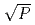 CORSOR-M model were confirmed for the pressures up to 16 MPa through comparison with the VEGA tests and mechanistic models, it is proposed that the model be used for source term analyses.
CORSOR-M model were confirmed for the pressures up to 16 MPa through comparison with the VEGA tests and mechanistic models, it is proposed that the model be used for source term analyses.
Hidaka, Akihide; Kudo, Tamotsu; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 91, p.499 - 500, 2004/12
The radionuclides release from MOX under severe accident conditions was investigated in the VEGA program to prepare the technical bases for safety evaluation including PSA for LWR using MOX. The MOX specimen irradiated at ATR Fugen was heated up to 3123K in He at 0.1MPa. The Cs release started at about 1000K and was enhanced below 2200K compared with that of UO . The possible reason is due to the formation of cracks connected to the high burn-up Pu spots. The total fractional releases were evaluated by alpha-ray, gamma-ray and ICP-AES and compared with the ORNL-Booth model. Although the model was prepared based on the tests with UO
. The possible reason is due to the formation of cracks connected to the high burn-up Pu spots. The total fractional releases were evaluated by alpha-ray, gamma-ray and ICP-AES and compared with the ORNL-Booth model. Although the model was prepared based on the tests with UO , the predictions are in reasonable agreement with the measurements. The VEGA test showed that the total releases from MOX are almost the same as those from UO
, the predictions are in reasonable agreement with the measurements. The VEGA test showed that the total releases from MOX are almost the same as those from UO under extremely severe accident conditions. This indicates that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO
under extremely severe accident conditions. This indicates that the consequences of LWR using MOX are mostly equal to those using UO . The effect of difference between MOX and UO
. The effect of difference between MOX and UO on the consequences will be systematically investigated using the JAERI's source term code, THALES-2.
on the consequences will be systematically investigated using the JAERI's source term code, THALES-2.
Ishikawa, Jun; Shintani, Kiyonori; Takagi, Seiji; Muramatsu, Ken
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Dai-8-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.203 - 208, 2002/00
no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide
RIST News, (30), p.2 - 14, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Ken; *; *; *; *
Dai-6-Kai Kakuritsuronteki Anzen Hyoka (PSA) Ni Kansuru Kokunai Shimpojiumu Rombunshu (IAE-9206), p.171 - 175, 1993/01
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Ken; *
Dai-6-Kai Kakuritsuronteki Anzen Hyoka (PSA) Ni Kansuru Kokunai Shimpojiumu Rombunshu (IAE-9206), p.3 - 8, 1993/01
no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide; *; Soda, Kunihisa; Muramatsu, Ken; Sakamoto, Toru*
ANS Proc. of the 1992 National Heat Transfer Conf., p.408 - 416, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
*; Muramatsu, Ken; Watanabe, Norio; *; *
Proc. of the Int. Topical Meeting on Safety of Thermal Reactors, 9 Pages, 1991/00
no abstracts in English